1. Making comparison: Branch vs Subsidiary vs Representative office in Hong Kong
Below are the main differences amongst the three widely-used registration options for foreign companies in Hong Kong:
1.1. Subsidiary in Hong Kong
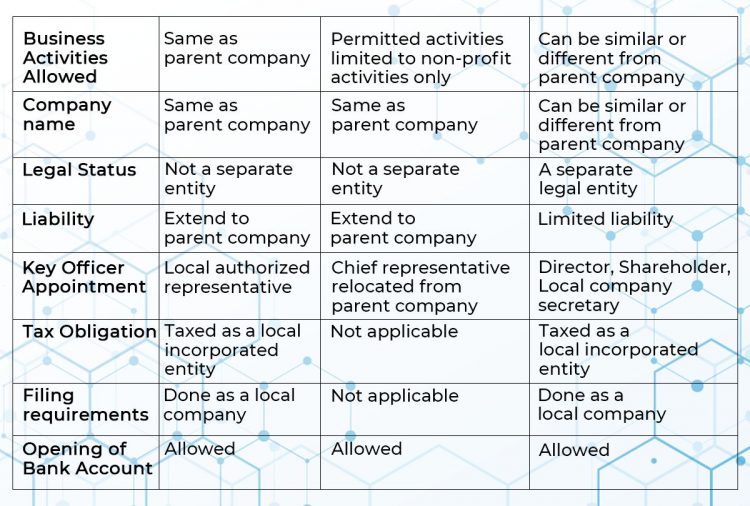
A subsidiary is a private limited company in nature. It can be owned by a maximum of 50 shareholders, each of whom can be an individual or a corporation.

The matter of liability
Since a subsidiary is basically a private company limited by shares, it is considered as a distinct legal entity that has a legal status separate from its owners/shareholders. This means if a foreign parent company holds ownership of a subsidiary in Hong Kong, it will not hold any further liabilities other than the proportion of shares it owns.
This can be a significant advantage since it provides a given foreign parent company with a great deal of safety in case everything goes south for its subsidiary in Hong Kong (insolvency for example).
Incorporation requirements
- Entity name: a subsidiary’s name can be similar or different to that of the parent company in another jurisdiction (however, subject to certain criteria).
- Business activity: a subsidiary can carry out activities that are the same or different from the parent company. This is an advantage over the types of branch and representative office.
- Entity’s key personnel: a subsidiary company in Hong Kong needs to satisfy the requirement of appointing the following key persons:
- One either local or foreign director;
- One either local or foreign shareholder; and
- One local resident company secretary
The process of setting up a subsidiary is quite similar to establishing a private company in Hong Kong. It can be done within a couple of days.
Learn more: How to set up a company in Hong Kong
Taxation
The taxation of a subsidiary is the same as a local private company in Hong Kong. Particularly, the profits of a subsidiary will be subject to two-tier corporate income tax (8.25% for the first 2 million HKD and 16.5% for remaining profits). Furthermore, it can be eligible for offshore tax exemption, meaning the profits earned from foreign sources will not be taxed in Hong Kong.
Related Article: How to take advantage of offshore tax exemption in Hong Kong
Compliance requirements
There is a number of post-registration requirements for a subsidiary in Hong Kong. Furthermore, on a yearly basis, the subsidiary must file a Tax Return together with audited accounts to the Inland Revenue Department and an Annual Return to the Companies Registry. Find out more: Hong Kong company annual compliance requirements
Note
The cost of incorporation in Hong Kong varies for different business types, structures, and industries. BBCIncorp has released a new Hong Kong Cost Planning Tool to work out initial costs for your business. Check it out!
Manage your business finances by working out all estimated cost for company setup, licenses, and so much more. 
COST PLANNING TOOL ![]() At-a-glance overview of business cost
At-a-glance overview of business cost ![]() Accessible and responsive consulting
Accessible and responsive consulting
1.2. Branch in Hong Kong
A branch office is deemed as only an extension of its parent company established in another jurisdiction.

The matter of liability
Since being only an extension, a branch office is not a separate entity in its own rights and powers, despite the fact that it is a legal entity registered with the Companies Registry. Hence, the foreign parent company will hold full responsibility for all debts or liabilities incurred by the branch office in Hong Kong.
Incorporation requirements
- Entity name: the name of a branch office in Hong Kong needs to be identical to that of the parent company.
- Business activity: a branch can only carry out a business activity that is the same as that of the parent company.
- Entity’s key personnel: For a branch setup, only one authorized representative who is a Hong Kong resident is required.
The requirements for a branch registration are rather few and easy. However, it is quite restrictive since the name and activity must be the same as its parent company.
Taxation
This is another similarity to a subsidiary. A branch in Hong Kong will be taxed in the same manner as local incorporated companies. It can also benefit from offshore tax exemption and Hong Kong’s network of international double tax treaties.
Compliance requirements
Likewise, a branch has to comply with many post-registration requirements. Furthermore, like local companies, it has to file annual reports to related Hong Kong’s regulatory authorities, sometimes a copy of the audited accounts of the parent company if requested.
For in-depth information: How to open a branch office in Hong Kong
1.3. Representative office in Hong Kong
A representative office is not treated as a legal entity since it is actually the office of its foreign parent company to be set up temporarily for administrative tasks in another jurisdiction – here to mention is the example of Hong Kong. It is worth noticing that a representative office in Hong Kong can only serve non-profit purposes.

The matter of liability
In most cases, due to having no legal standing, a representative office does not bear any liability in event of costs of debts. All the liabilities will be channeled back to its foreign parent company.
Incorporation requirements
- Entity name: the name of a representative office in Hong Kong needs to be identical to that of the parent company.
- Business activity: a representative is not allowed to earn profits, it is only allowed to carry out non-profits activities such as market research or administrative tasks.
- Entity’s key personnel: a representative office is only required to appoint a staff member from the overseas parent company to relocate to Hong Kong.
Taxation
Since no profit can be generated from a representative office in Hong Kong, no tax is imposed on such office.
Compliance requirements
Likewise, it is not required in compliance requirements of filing tax returns or annual returns with competent authorities like others. Note, however, that application for a Business Registration Certificate (including renewals of Certificate) is still a mandatory requirement for the representative office in Hong Kong.
Our related article on An introduction to Hong Kong representative offices will walk you through more useful information!
2. How to choose the best business structure for your foreign company
Whether you decide on a branch office, a representative office or a subsidiary, you should in advance well consider your foreign parent company’s business goals, as well as the positives and negatives of each structure.
Below are some considerations for you:
- It appears to be common that large corporations often let a slight bias towards opening a branch office, while most SMEs companies are more likely to choose a subsidiary or a representative office in Hong Kong.
- Branch office and subsidiary are in line with those engaging in profit-earning activities. However, the disadvantages of these two are their continuing compliance obligations namely audited accounts, filing annual return and tax returns, AGMs, etc.
- Both branch office and subsidiary company bear no difference in the tax rates applied. Both are taxed as locally incorporated companies in Hong Kong.
- Representative offices act as a temporary vehicle. Despite the fact that it is not taxed by virtue of its non-profit making nature and less subject to compliance requirements than other business structures, it cannot generate any revenue for the foreign parent company.
- In case of a subsidiary, its parent company’s liability is limited to the amount of share capital contributed to the subsidiary, whereas a branch office and representative office have their liabilities extending to their parent company.
Still uncertain about branch vs subsidiary vs representative office in Hong Kong – which type of business presence is best suited for your foreign company? Feel free to email us your queries for more useful advice!



